I met my best friend Paul in 1970 on the first day of Grade 1. Like my best friends in high school, college, and law school, Paul turned out to be gay. (Apparently I’m contagious.)
Paul also turned out to be mentally ill. After struggling with depression, anxiety, and other challenges, Paul killed himself twenty years ago.
I thought of my friend Paul while reading the first chapter of Stephanie Foo’s recent memoir. A few months before he died, Paul told me he felt betrayed by his healthcare providers. While peeking at his medical charts, he discovered he had Borderline Personality Disorder, a bleak diagnosis that was even bleaker two decades ago. No one bothered to tell Paul, which made it even worse.
In What My Bones Know: A Memoir of Healing from Complex Trauma, Foo writes about growing up in San Jose with dysfunctional immigrant parents who subjected her to relentless physical and emotional abuse before abandoning her as a teenager. Foo escaped to college, found an effective therapist, and went on to a successful career in Bay Area public radio. Eventually Foo moved to New York to work as a producer at This American Life, the granddaddy of podcasts.
Nevertheless, Foo found herself increasingly frustrated with challenges at work and in her relationships. At age thirty she was still seeing the same therapist, now via Zoom. Eventually she asked “Do you think I’m bipolar?”
Samantha actually laughs. “You are not bipolar. I am sure of it.” she says. And that’s when she asks, “Do you want to know your diagnosis?”
I don’t yell, “Lady, I've been seeing you for a fucking decade, yes I want to know my goddamn diagnosis,” because Samantha taught me about appropriate communication. Thanks, Samantha. Instead, I say, “Yes. Of course.”
Something in her jaw becomes determined, and her gaze is direct. “You have complex PTSD from your childhood, and it manifests as persistent depression and anxiety. There’s no way someone with your background couldn’t have it,” she says.
“Oh. Yeah, PTSD.” Post-traumatic stress disorder. I had a crappy childhood, so I kinda figured that.
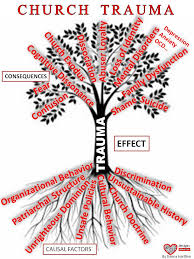
“Not just PTSD. Complex PTSD. The difference between regular PTSD and complex PTSD is that traditional PTSD is often associated with a moment of trauma. Sufferers of complex PTSD have undergone continual abuse-trauma that has occurred over a long period of time, over the course of years. Child abuse is a common cause of complex PTSD,” she says. Then her eyes drift to the corner of the screen. “Oh—we're out of time! Let’s continue this next week.”
We’ve recognized for millennia that wartime trauma causes a predictable constellation of physical and mental symptoms. In the 4000-year old Epic of Gilgamesh, the warrior-hero experiences intrusive memories and nightmares after witnessing the death of his best friend. Greek historian Herodotus described an Athenian soldier who was stricken with blindness in 490 B.C. when he observed the death of a comrade at the battle of Marathon. After the Civil War, veterans developed “soldier’s heart.” The term “shell shock” first appeared in The Lancet in February 1915, six months after World War I began.
Seven years ago I moved to Bellingham to accept a position with the Washington Attorney General’s Office as general counsel to Western Washington University. My dream job became a nightmare when I began exhibiting strange new symptoms, including bizarre anxiety tics and skewed personal interactions. I was shocked when my new Bellingham physician, Dr. Heuristic, diagnosed me with PTSD and serious codependency.
As I told a friend who developed PTSD after serving as an Army Ranger medic in Afghanistan, I was sheepish about sharing the same DSM-5 category with someone like him. He told me not to be concerned, and that soldiers feel lucky they get so many folks’ respect. They worry instead about the many women and children who are scarred by the impact of earlier domestic abuse and do not have access to the help they need.
Or as Stephanie Foo writes:
It is a great, sexist irony that in our society, PTSD is generally considered a male condition. It is the warrior's disease, a blight of the mind that must be earned by time in battle, in some dangerous overseas desert or jungle. But the real statistics suggest the opposite: Women are more than twice as likely to have PTSD than men. Ten percent of women are expected to suffer from PTSD in their lifetimes, as opposed to just 4 percent of men. But even after #Me Too, a global movement to recognize the legitimacy of women's trauma, treatment for this trauma remains a half-assed endeavor, an afterthought in the shadow of the glory of war. And it has always been this way.

Actually, it usually has been even worse.
Bessel van der Kolk is one of the world’s leading experts in trauma and its treatment. In his classic book The Body Keeps the Score: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of Trauma, Dr. van der Kolk describes how both sides in World War I mistreated their traumatized soldiers. Depending on the whims of individual doctors, British servicemen originally would either get a diagnosis of “shell shock,” which entitled them to treatment and a disability pension, or “neurasthenia,” which got them nothing. Then in June 1917, the British General Staff issued an order stating “In no circumstances whatever will the expression ‘shell shock’ be used verbally or recorded in any regimental or other casualty report, or any hospital or other medical document.” According to Dr. van der Kolk, “The Germans were even more punitive and treated shell shock as a character defect, which they managed with a variety of painful treatments, including electroshock.”
During World War II, my grandfather’s generation benefited from more humane leadership and more effective psychiatric treatments. They also had the benefit of fighting and winning a “good war,” followed by the GI Bill and fifty years of peace and prosperity. Meanwhile, individuals and society mostly repressed the lingering impact of wartime trauma.
In contrast, Vietnam was a “bad” war in every way, which likely amplified its traumatic impact on American veterans. When Dr. van der Kolk began his medical career with the Veterans Administration during the 1970s, he was struck by the fact that all his psychiatric patients were “young, recently discharged Vietnam veterans,” even though the VA hospital was filled with aging WWII vets who were all being treated for purely “medical” complaints: “My sense was that neither the doctors nor their patients wanted to revisit the war.”
In a sign of the times, the term “Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder” was coined in 1978. The diagnosis was added to the DSM-III in 1980, with criteria that continue to reflect its status as an event-based disorder.
Dr. van der Kolk is the founder of the Trauma Research Foundation and the National Child Traumatic Stress Network. Although his work began with Vietnam veterans, he quickly recognized trauma also affects other vulnerable populations. In particular, “child abuse and neglect is the single most preventable cause of mental illness, the single most common cause of drug and alcohol abuse, and a significant contributor to leading causes of death such as diabetes, heart disease, cancer, stroke, and suicide.”
As the Department of Veteran’s Affairs recognizes, “Many traumatic events (e.g., car accidents, natural disasters, etc.) are of time-limited duration. However, in some cases people experience chronic trauma that continues or repeats for months or years at a time.” In 1988, Dr. Judith Herman proposed a new diagnosis of “complex PTSD.” In addition to the symptoms associated with classic PTSD, complex PTSD includes:
- Behavioral difficulties (e.g. impulsivity, aggressiveness, sexual acting out, alcohol/drug misuse and self-destructive behavior)
- Emotional difficulties (e.g. affect lability, rage, depression and panic)
- Cognitive difficulties (e.g. dissociation and pathological changes in personal identity)
- Interpersonal difficulties (e.g. chaotic personal relationships)
- Somatization (resulting in many visits to medical practitioners)
Rather than a single traumatic event, complex PTSD is a consequence of ongoing trauma that occurs over an extended period, such as childhood abuse and neglect, domestic violence, and religious trauma. Because these types of experiences tend to involve betrayals by an individual’s most trusted authority figures, the resulting symptoms focus on impaired interpersonal relationships. Although the DSM-5 does not include diagnoses for complex PTSD or codependency, complex PTSD is already recognized by the Department of Veterans’ Affairs, the World Health Organization, and the British National Health Service.
Here is Stephanie Foo's reaction when she ended the Zoom call with her therapist and found the VA webpage after googling “complex PTSD”:
It is not so much a medical document as it is a biography of my life: The difficulty regulating my emotions. The tendency to overshare and trust the wrong people. The dismal self-loathing. The trouble I have maintaining relationships. The unhealthy relationship with my abuser. The tendency to be aggressive but unable to tolerate aggression from others. It’s all true. It’s all me. The more I read, the more every aspect of my personhood is reduced to deep diagnostic flaws. I hadn’t understood how far the disease had spread. How complete its takeover of my identity was. The things I want. The things I love. The way I speak. My passions, my fears, my zits, my eating habits, the amount of whiskey I drink, the way I listen, and the things I see. Everything—everything, all of it—is infected. My trauma is literally pumping through my blood, driving every decision in my brain.
It is this totality that leaves me frantic with grief. For years I’ve labored to build myself a new life, something very different from how I was raised. But now, all of a sudden, every conflict I’ve encountered, every loss, every failure and foible in my life, can be traced back to its root: me. I am far from normal. I am the common denominator in the tragedies of my life. I am a textbook case of mental illness. Well, this explains it all, I think. Of course I’ve been having trouble concentrating on my work. Of course so many people I've loved have left. Of course I was wrong to think I could walk into fancy institutions full of well-bred, well-educated people and succeed. Because the person with C-PTSD, the person who is painted here on the internet, is broken.
Stephanie Foo’s bleak epiphany comes near the beginning of her story, which is subtitled “A Memoir of Healing from Complex Trauma.” Eventually she recognized her disability had clouded her vision, and learned that healing is “the opposite of the ambiguous dread: fullness.
I am full of anger, pain, peace, love, of horrible shards and exquisite beauty, and the lifelong challenge will be to balance all of those things, while keeping them in the circle. Healing is never final. It is never perfection. But along with the losses are the triumphs. I accept the lifelong battle and its limitations now. Even though I must always carry the weight of grief on my back, I have become strong.
Foo’s “inner narrative” finally changed “from a hateful whip-bearing tyrant to a chill(er) surfer dude. Like love and bankruptcy, it happened slowly, then all at once.”
In many ways my journey through complex trauma and PTSD parallels Foo’s. Both of us escaped from our abusive origins by joining demanding professions – journalism and law – that turned out to be toxic. Yet we both found healing through writing, with the support of true friends and expert healthcare providers.
Nevertheless, my experience with complex PTSD differs from Foo’s in important respects. Like so many other trauma victims, Foo’s symptoms are rooted in the pattern of abuse she suffered at the hands of her own family. I am an outlier because I was betrayed by a different kind of trusted authority figure – the Mormon priesthood leaders who told me homosexuality was a spiritual disease that could be “cured,” and who continue to deny the humanity and existence of LGBT individuals today. Fortunately, in contrast with most people who struggle with complex PTSD symptoms, I had and have the support of the best family in the world. But I also had the traumatic overlay of coming out of the closet at the height of the AIDS epidemic, when silence and rage both equaled death.
In contrast with Stephanie Foo, no one ever told me “There's no way someone could come from your background and not have complex PTSD.” Who can predict something like that? As every personal or global disaster demonstrates, individual responses to trauma will vary. What I do know is there’s no way someone could come through all this and not be a trauma survivor. If they weren’t survivors, they wouldn't have made it through – as so many of my tribe can attest. Those of us who remain.
My friend Paul’s anger at his healthcare providers probably contributed to his suicidal distress. Stephanie Foo reacted to her belatedly revealed diagnosis not only with rage, but also with resolve:
After I started realizing the magnitude of what having C-PTSD meant, I was livid at Samantha for not telling me about it sooner. This should not have been a secret, I thought. My diagnosis should have been a critical part of the conversation about my mental health this entire time.
So Foo fired her longtime therapist and began treatment with a New York psychiatrist who is one of the world’s experts in complex PTSD.
Why don’t I complain about my doctor’s original label for my disability seven years ago? Because he got it right. As I’ve reported from the beginning, after hearing about my symptoms and my background, Dr. Heuristic diagnosed me with “PTSD and serious codependency.” In addition to referring me to a therapist who specialized in treating PTSD, he also directed me to read Facing Codependency by Pia Mellody, and to attend weekly meetings sponsored by Codependents Anonymous (“CODA”). Because of my doctor’s experience with the recovery community, he recognized I would benefit from CODA’s group therapy model.
As the term is used by CODA, “codependency” refers to a pattern of deeply rooted compulsive behaviors that interfere with individuals’ ability to sustain healthy relationships, maintain functional boundaries, and express their reality appropriately. These are the same symptoms that distinguish complex PTSD from the “classic” PTSD diagnosis in the DSM. At the beginning of each CODA meeting, everyone recites the words “Many of us were raised in families where addictions existed - some of us were not.” I’m one of the “some of us.” It turns out being gay among the Mormons can be more harmful than growing up in a saloon.
 |
| Paul and Roger in Grade 4 |
Labels are not the patient.
This year I’ve been reading through all of Oliver Sacks’ books. Dr. Sacks, a distinguished neurologist who died in 2015, was an extraordinary observer of the great diversity in human thinking. Most recently I finished his classic The Man Who Mistook His Wife for a Hat, a fascinating collection of case studies. In the introduction, Dr. Sacks writes that when he was a young medical student
it was the patients I saw, their predicaments and their stories, that gripped my imagination, and these experiences imprinted themselves upon me indelibly. Lectures and textbooks, abstracted from living experience, left almost no impression. I was, however, strongly drawn to the case histories that abounded in the nineteenth-century medical literature-rich, detailed descriptions of patients with neurological or psychiatric problems. It is only by accumulating case histories of people with similar syndromes, comparing and contrasting them, that one can more fully understand the mechanisms involved and their resonances for an individual life…. With the rise of neuroscience and all its wonders, it is even more important now to preserve the personal narrative, to see every patient as a unique being with his own history and strategies for adapting and surviving.
Since moving to Bellingham, my family has been blessed with exceptional caregivers. In particular, my physician has guided my recovery with insight and compassion. He immediately figured out my weird symptoms added up to Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder and codependency. He correctly diagnosed my tennis elbow and plantar fasciitis. He’s much nicer than Dr. House, the abrasive but insightful head of TV’s fictional “Department of Diagnostic Medicine.” He doesn’t laugh at my jokes about suing people for malpractice, but doctors never do.
I originally gave my doctor his nickname because a “heuristic” is a simple procedure that our brains use to find quick answers to difficult questions. An expert’s various heuristics add up to an effective algorithm. Eventually I figured out my doctor’s heuristic for me. Whenever I show up with some new complaint, he will generally select from a repertoire of three standard responses:
- It's just another typical PTSD symptom.
- It’s a common side effect of my medications.
- It’s what happens when we get older. (He calls these “barnacles.”)
Nevertheless, Dr. Heuristic isn’t trapped by diagnostic categories. He sees each patient as an individual. He’s the opposite of the lawyers that surround me, who are blinded by confirmation bias, and so in love with the sound of their own voices that they cannot hear my scratchy lament. Because my doctor pays attention, he can help his patients find the answers they need. Rather than “Dr. Heuristic,” perhaps a better label for my insightful physician would be “Dr. Epiphany.”






Thank you for posting this. I really needed to read this tonight.
ReplyDelete—another lawyer with a mental health disability